Natural gas is a gas that is widely used In today's world. They are particularly crucial in many aspects of daily life and production. What exactly is natural gas, what makes up its many components, and how is it used in both production and daily life? In the article that follows, let's learn more about natural gas with Gas South!
1. What is Natural Gas?
Natural gas is a common term for a fossil fuel primarily composed of hydrocarbons, which are chemical compounds containing hydrogen and carbon. It can be found and extracted from oil deposits deep within the Earth's crust or gas fields.

Natural gas is one of the most important fossil fuels
2. What is the Main Component of Natural Gas?
Natural gas is mostly composed of methane (85%), ethane (10%), and tiny quantities of pentane (5%), butane (4%), propane (3%), and other alkanes (alkanes).
Natural gas compositions may also include trace quantities of other contaminants such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulfide.
In natural gas, substances that aren't hydrocarbons are referred to as impurities and diluents. Hydrogen sulfide and sulfur compounds are typical pollutants that can harm and taint manufacturing and transportation machinery. These compounds can contribute to air pollution and acid rain when they are burnt. Thinners, such as nitrogen, water vapor, and carbon dioxide, are frequently eliminated during the purification of natural gas.
2.1 Classification of Natural Gas
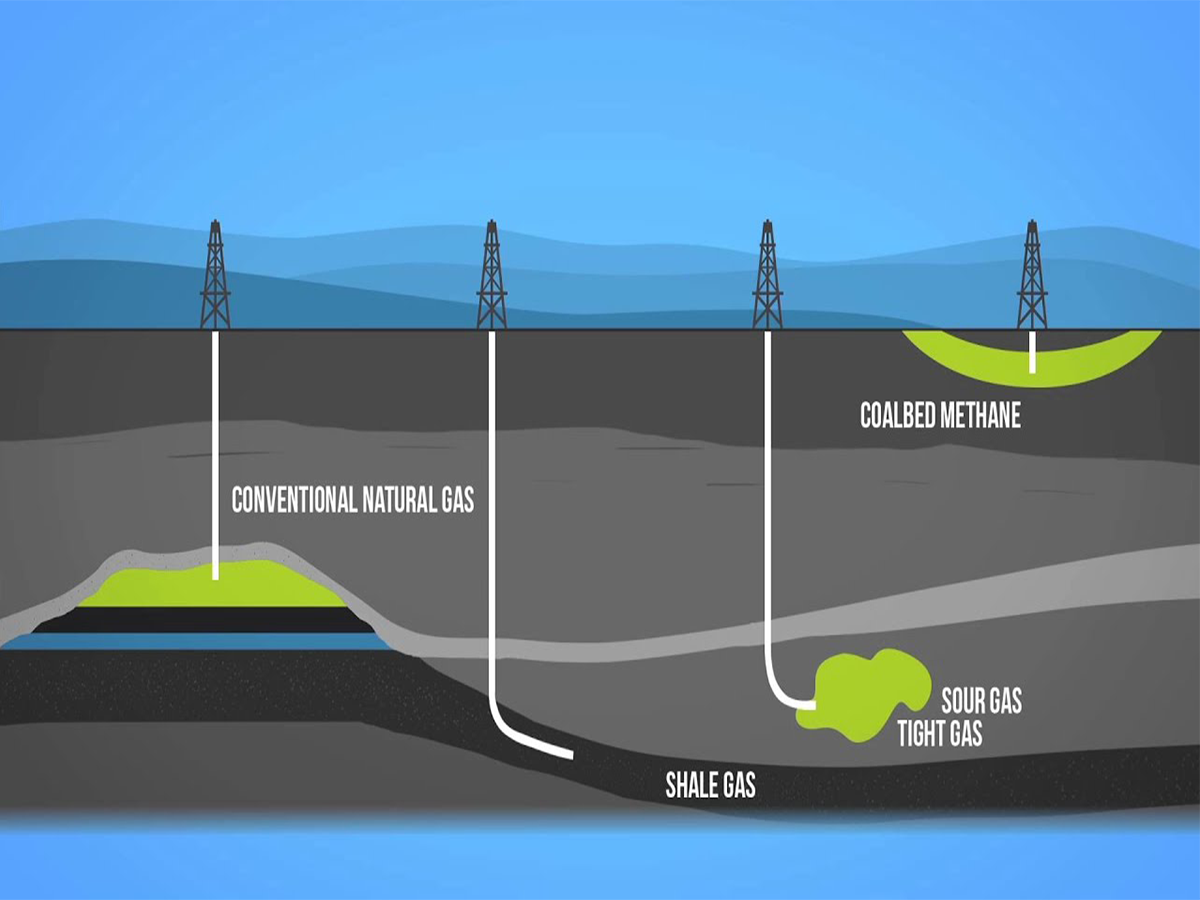
Natural gas is a colorless gas mixture that is classified based on its chemical composition. Specifically, natural gas is divided into four main types as follows:
-
Dry gas: This type of natural gas contains a high proportion of methane in its composition.
-
Wet gas: This type of natural gas contains a higher proportion of higher hydrocarbons such as ethane, butane, and propane compared to dry gas.
-
Sour gas: This type of natural gas contains a high concentration of hydrogen sulfide in its composition (hydrogen sulfide is a toxic gas with the smell of rotten eggs).
-
Sweet gas: This is natural gas with a low concentration of hydrogen sulfide in its composition.
3. Differentiating Crude Oil and Natural Gas
Crude oil is a thick liquid that is typically black or dark brown in color, lighter than water, and insoluble in water. In nature, crude oil is usually found in large deposits deep underground, forming oil fields. An oil field consists of three layers: a gas layer on top (also known as associated gas) primarily composed of methane, a liquid oil layer containing mainly hydrocarbons along with small amounts of impurities, and a salty water layer at the bottom. Crude oil is a valuable fossil resource, and its distilled products have various applications in daily life, including gasoline, diesel, natural gas, and asphalt.
Natural gas is a gas mixture that is extracted from natural gas fields deep underground or from the gas layer (associated gas) above crude oil deposits. The primary component of natural gas is methane, along with small amounts of other hydrocarbons. Similar to crude oil, natural gas is also considered a significant fossil resource. In everyday life and industry, natural gas is commonly used as a fuel and feedstock.
4. Where does Natural Gas Typically Originate and Where Is It Concentrated?
Natural gas constitutes Aquatic plankton, comprising protozoa and algae. When these species pass away, their remains amass on the ocean floor and are progressively covered by sedimentary layers. Natural gas was chemically created from the organic stuff in the plankton's body over the course of millions of years under the intense heat and pressure brought on by the superposition of sediments.
Natural gas and petroleum slowly seeped into the surrounding openings and microscopic pores of the porous rock layer during the deposition process over millions of years, generating vast oil and gas fields. As a result, natural gas can be found in oil fields or gas fields that are located far below the Earth's surface. A sizable amount of natural gas is also present in the coal strata. Frequently, they are dispersed across the coal bed's fissures and fractures.
Natural gas is currently being found on all of the world's major continents (apart from Antarctica). The world's total natural gas reserves are thought to be 150 billion trillion cubic meters. The Middle East has the second-largest volume, at roughly 50 billion cubic meters, while the remaining natural gas reserves are spread over numerous different regions in the Americas, Asia, and Australia.
 Russia is the country with the largest natural gas reserves in the world
Russia is the country with the largest natural gas reserves in the world
5. The Process of Natural Gas Exploitation
Geologists must first pinpoint the precise location of gas fields using the relevant geological characteristics and indicators for gas production in order to extract natural gas. Once the site has been established, gas may be extracted by drilling directly through the permeable rock layer underneath. When the pressure inside the porous rock layer weakens over time, natural gas must be sucked to the surface using a pump. Initially, natural gas will be forced up onto the well mouth depending on the pressure inside that layer.
Natural gas extraction in gas fields
Gas pipelines transport liquefied natural gas from the subsurface to refineries where it is processed. Non-hydrocarbon contaminants are eliminated during this procedure (most notably carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide). After the removal of impurities is complete, natural gas is transported to the consumer areas, which are residential areas, industrial zones, or as raw materials in the petrochemical industry.
6. Utilization of Natural Gas in Daily Life
Natural gas is one of the non-renewable fossil fuels which has a wide range of uses in both production and daily living, including the following:
-
Gas furnaces in enterprises that produce dry goods or food can be powered by natural gas.
-
Used as a fuel in industrial kilns including cement plants, brick kilns, metallurgical furnaces, and ceramic kilns.
-
Used as a combustion fuel in thermal power plants to produce heat to turn turbines.
-
The petrochemical sector uses natural gas-derived propane, ethane, and butane as key raw ingredients to generate essential goods like plastics, detergents, and medicines.…
-
By exposing the bacteria such as methylococcus capsulatus to natural gas, it is used to produce fish feed and protein feed.
-
Used as a fuel for motors that use H2 or to create H2 gas, an essential raw material in many industries.
-
Used as a fuel in compressed or liquefied natural gas-powered motors.

Transporting natural gas using tanks
7. Is Natural Gas Environmentally Harmful? Understanding the Environmental Effects
Even though it is regarded as clean fossil fuel and produces less pollution than coal and oil. However, the extraction, refinement, and use of natural gas can have a detrimental impact on the environment in the following ways:
-
Hydrogen sulfide in sour gas, if not thoroughly filtered, can cause air pollution and generate acid rain.
-
During the exploitation process, natural gas fields will experience pressure reduction, creating subsidence that will harm the ecology of the surrounding region. Another hazardous gas that can be fatal if breathed excessively is hydrogen sulfide.
-
If there is no vent or leak, using natural gas for heating might result in CO poisoning. In addition, excessive exposure to natural gas in confined spaces can result in asphyxiation and lung damage.
-
Natural gas leaks can result in explosive combustion that harms both people and property.
-
Natural gas exploitation may result in the creation of radioactive materials like polonium, lead, and radon that are hazardous to human health.
-
Even though using natural gas can result in 40% to 45% less carbon dioxide than burning coal or petroleum, it still has a sizable impact on the rise of greenhouse gas emissions. Despite having a short half-life (about 7 years), methane is nevertheless regarded as a powerful greenhouse gas that raises global temperatures.
Gas South has provided you with some useful information regarding natural gas in this short post. After reading this post, perhaps you have a better grasp of how to use natural gas in your daily life and for production. Currently, Gas South is a provider of renowned and high-quality natural gas in Vietnam at the most affordable pricing. Customers can speak with Gas South directly through the following channels to ask questions and get a price for liquefied natural gas (LNG):
-
Southern Gas Trading Joint Stock Company - Gas South
-
Head office: 4th Floor, PetroVietnam Tower, Le Duan, Ben Nghe Commune, District 1, Ho Chi Minh City
-
Phone: 028.3910 0108 - 025.3910 0324
-
Email: lienhe@pgs.com.vn
-
Hotline: 18006776
Please call the hotline for guidance and a full quote if you need to learn more about or purchase compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG)!


